From the Open-Publishing Calendar
From the Open-Publishing Newswire
Indybay Feature
WorkWeek on Hiroshima Anniversary, E. Palestine Poisoning, LA Meeting on Fascism & Workers
WorkWeek on KPOO covers Hiroshima Anniversary, E. Palestine Poisoning, LA Meeting On Fascism & Workers Party & Slave Labor & Free Labor In The Golden State With Professor Jean Pfealzer
WorkWeek On Hiroshima Anniversary, E. Palestine Poisoning, LA Meet On Fascism & Workers Party & Slave Labor & Free Labor In The Golden State With Professor Jean Pfealzer
WorkWeek looks at the anniversary of the bombing of Hiroshima on August 6.
A rally was held in front of the Japanese consulate in San Francisco to protest the continued militarization of Japan and Asia.
Despite Japanese constitution Article 9 which forbids offensive war the Kishida government and the previous Abe government have expanded the military and supported continued US military bases in Okinawa that the people are opposing.
WorkWeek also looks at the continued contamination of the people and workers of East Palestine,Ohio from a derailment last February 2023 by Norfolk Southern is bringing anger and frustration. The company ignited tank cars containing vinyl chloride despite the owner of the toxin sayin that they should not blow up the chemical.
According to Jame Rae Wallace who was the past president of Cleveland State University SEIU 1199 and a resident they were lied to by the company and the EPA about the danger of the toxin and are now being coerced to support a settlement agreement and class action that will not provide healthcare benefits and compensation for their homes to move out of the contaminated town.
WorkWeek looks at the growth of a fascist movement in the US and what that means for
unions and workers in the US.
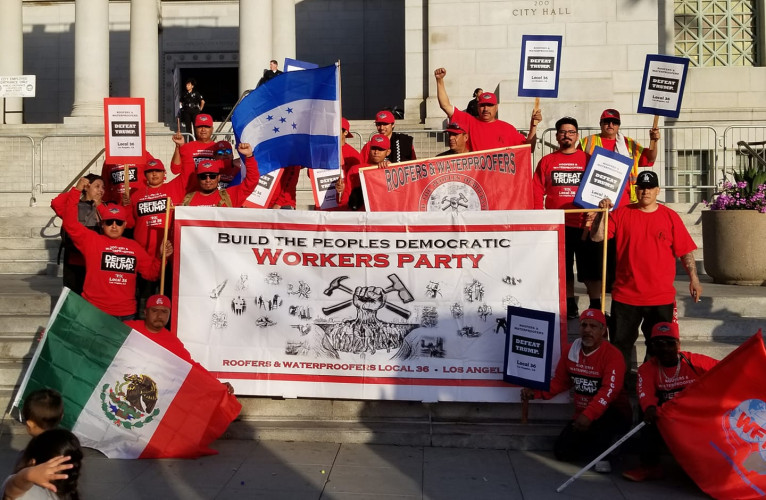
WorkWeek interviews Cliff Smith who is the business manager of Roofers Local 36 in Los
Angeles. Trump and his supporters have already said that they will not accept an election
unless they win it and they have already organized an attempted coup and insurrection.
Smith and his local is planning a meeting in Los Angeles on September 7th to discuss
the rise of fascism, democracy and the formation of a workers party.
WorkWeek On Slave Labor & Free Labor In The Golden State With Professor Jean Pfealzer
https://soundcloud.com/workweek-radio/ww-8-15-24-slave-labor-free-labor-in-the-golden-state-with-professorjean-pfealzer
WorkWeek hears a presentation by Jean Pfealzer, a professor and author of California A Slave State on slave labor and free labor in California . She discussed the history of slavery in California from the Spaniards and the Missions to the Russians and then slavery when California became a state..
This presentation was part of Laborfest which commemorates the San Francisco general strike and it was held at the Angel Island immigration station where tens of thousands of immigrants including many Chinese arrived in the United States.Pfealzer besides the author of California A Slave State is also author of Driven Out:The Forgotten War Against Chinese Americans.
Additional Media:
California A Slave State With Jean Pfaelzer
https://youtu.be/JjMisZzA-n0
The History Of Slavery In California With Professor Jean Pfealzer
https://youtu.be/tfgQU0qig6Y
Additional Info:
https://www.jeanpfaelzer.com
https://soundcloud.com/workweek-radio
workweeknow [at] gmail.com
#laborradionetwork #LaborRadioPod #1u #UnionStrong
Hidden Report Reveals How Workers Got Sick While Cleaning Ohio Derailment Site
https://time.com/7011096/workers-sick-cleaning-ohio-derailment-site/
Debris from a Norfolk Southern freight train lies scattered and burning along the tracks, Feb. 4, 2023, the day after it derailed in East Palestine, Ohio. Gene J. Puskar—AP
BY ASSOCIATED PRESSAUGUST 14, 2024 3:31 PM EDT
The creeks around East Palestine, Ohio, were so badly contaminated by last year's disastrous Norfolk Southern derailment that some workers became sick during the cleanup.
Workers who reported headaches and nausea — while shooting compressed air into the creek bed, which releases chemicals from the sediment and water — were sent back to their hotels to rest, according to a report obtained by The Associated Press about their illnesses.
The findings were not released to the public last spring, despite residents' concerns about the potential health effects of exposure to the long list of chemicals that spilled and burned after the disaster. The workers' symptoms, as described in the report, are consistent with what Centers for Disease Control and Prevention workers going door-to-door in town had reported shortly after the Feb. 3, 2023, derailment.
Read more: East Palestine, One Year After Train Derailment
Since then some residents have also reported unexplained rashes, asthma and other respiratory problems, and serious diseases including male breast cancer.
Researchers are still determining how many of those health problems can be linked to the derailment and how the disaster will impact the long-term health of residents in the area near the Ohio-Pennsylvania border. Many wonder whether there will be cancer clusters down the road, which of course won't be clear for years.
In the meantime, residents have until Aug. 22 to decide whether to accept up to $25,000 — as part of a $600 million class action settlement with the railroad to compensate them for any future health problems. Accepting that money though means giving up the right to sue later, when the cost of health care coverage and specific treatments needed will become more clear.
Norfolk Southern spokesperson Heather Garcia said none of the workers who got sick during the cleanup “reported lingering or long-term symptoms."
“The health and safety of our employees, contractors, and the community has been paramount throughout the recovery in East Palestine,” Garcia said.
The creek cleanup work continued, but nearly three weeks later, another worker got sick. This time, it was halted altogether. While there've been other cleanup projects since then, they've stopped using high-pressure air knife tools.
Independent toxicologist George Thompson who has been following the aftermath of the Ohio wreck said the cleanup contractors, overseen by the Environmental Protection Agency, should have known the work they were doing would release chemicals from the sediment into the air and water. In fact, that is what CTEH was monitoring while the project was underway. And with one of the main streams, Sulphur Run, going directly through town and in culverts under homes and offices, Thompson said those chemicals could have infiltrated buildings.
“You’re just spreading out the chemicals for exposure,” Thompson said. “And I just think that it was not an informed decision to use air knifing at all.”
Resident Jami Wallace said she lost her voice for two weeks after she got too close to one of the air knifing machines, which was placed near her driveway. She said when the machine was turned on, it felt like being hit by an invisible wall emitting a sweet chemical smell much like when the train derailed.
The report from CTEH was submitted to Unified Command, the group overseeing disaster response — which included federal, state and local officials along with Norfolk Southern — but no one released it despite significant public interest. CTEH's principal toxicologist Paul Nony confirmed the report was given to the command center, and officials there were alerted about the illnesses.
When CDC workers got sick — also with headaches and nausea — it generated headlines nationwide.
East Palestine resident Misti Allison said not enough is being done to monitor long-term health effects on the community, and this report substantiates their health concerns. She said this report should have never been kept from the public.
“It’s absolutely egregious, and that shouldn’t happen. I think that any type of information like that — just like when the CDC workers came to the area and got sick — that should be disclosed instead of diminished,” Allison said. “Especially when it comes to human health, nothing should be swept under the rug.”
The East Palestine derailment that happened on the night of Feb. 3, 2023, was easily the worst rail disaster since a crude oil train leveled the small Canadian town of Lac Megantic and killed 47 people in 2013. It prompted a national reckoning with rail safety and calls for reform — although proposals for new industry rules have stalled in Congress.
Thirty-eight cars derailed, including 11 carrying hazardous materials such as butyl acrylate and vinyl chloride. After the crash, a fire burned for days. Fearing the five vinyl chloride cars would explode, officials then needlessly blew them open, and intentionally burned the toxic plastic ingredient.
That created a massive plume of thick black smoke over the area. The NTSB determined that the decision-makers that day never received the key opinion — that the cars were not likely to explode — from the chemical manufacturer.
The major freight railroads responded by pledging to add hundreds more trackside detectors nationwide to help spot mechanical problems. They also reevaluated the way they respond to alerts and even before alerts, the way they track rising temperatures from an overheating wheel bearing.
This summer’s completion of the NTSB investigation into the crash brought renewed hope that Congress might pass a rail safety bill, but little action has been taken outside of a House hearing on the subject last month.
CTEH said that its environmental testing around the creeks confirmed there were elevated levels of an assortment of chemicals in the air and sediment. Still, the group didn't find either of the two chemicals of greatest concern: vinyl chloride or butyl acrylate. Sediment testing at nine locations along the creeks where cleanup workers reported strong odors did show 37 different chemical compounds that were primarily either hydrocarbons or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Because of that, CTEH said it was clear that some of the contamination in the creeks came from industries that operated in the area years before the 2023 derailment. Still, those compounds could have also been created from chemicals burning after the train crash.
Nony, the head CTEH toxicologist, said that his company's responsibility during the air knifing operation was primarily to monitor air quality.
The EPA has said that it doesn't believe people are being exposed to any toxic chemicals on an ongoing basis because concerning levels of chemicals haven't been found in their air and water tests since the evacuation order was lifted.
In follow-up testing this year, the agency did find small amounts of vinyl chloride and other chemicals at the crash site, but citing only small amounts and the fact that the contaminated soil was removed, the agency said they don't represent a risk to human health.
The overall clean up effort in East Palestine is expected to be completed sometime later this year.
How a US health agency became a shield for polluters
https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/usa-pollution-atsdr-landfill/
How a US health agency became a shield for polluters
Companies and others responsible for some of America's most toxic waste sites are using a federal health agency’s faulty reports to save money on cleanups, defend against lawsuits and deny victims compensation, a Reuters investigation found. A Missouri neighborhood's tale.
By JAIMI DOWDELL, M.B. PELL, BENJAMIN LESSER, MICHELLE CONLIN, PHOEBE QUINTON and WAYLON CUNNINGHAMFiled Aug. 7, 2024, 11 a.m. GMT
William Wright
Non-Hodgkins lymphoma
Jean Nowlin
Breast cancer
Kathleen Schindler
Breast cancer
Melanie Sue Herberger
Lung cancer
Mary Patricia Sanguinet
Breast cancer
Martha Kowalczyk
Breast and lung cancer
Kathleen Ann Laube
Breast cancer
Donald Wagner
Pancreatic and prostate cancer
Mark Tinker
Brain cancer
Valerie Shelton
Kidney cancer
Janice Majka
Pancreatic cancer
Robert Majka
Lung cancer
Deborah Mitchell
Colorectal cancer
Fred Ingrim
Lung cancer
Arthur "Rex" Cornett
Lymphoma
Joan Cornett
Breast and liver cancer
Becky (Baum) Davis
Breast cancer
Julie Renee (Baum) Glenn
Breast cancer
Thomas Baum
Lung cancer
Diana Baum
Breast cancer
Charles Stafford
Colon cancer
Harold Krueger
Pancreatic cancer
Evelyn Krueger
Esophogeal cancer
Martha Wilson
Lung and bladder cancer
John Elton James
Esophogeal cancer
JoAnn Arter
Lung cancer
Michelle Herbel
Cervical cancer
Deborah Ann Berry
Pancreatic cancer
Linda Calvo
Bladder cancer
Patricia "PattytheK" Bott
Breast cancer
Dennis Hoppe
Stomach, esophogeal, liver and lung cancer
Carroll Edward Johns
Colon cancer
Deborah Jane Winston
Kidney cancer
Westlake Landfill
Spanish Village
When they bought their homes in the Spanish Village neighborhood northwest of St. Louis, many residents had no idea a radioactive landfill sat less than a mile away.
Health conditions mounted over the years, suggesting something wasn’t right.
Reuters reporters tracked down current or former residents of half of the neighborhood’s 92 homes. At least 33 of those people have been diagnosed since the 1980s with types of cancer that have been linked to radiation.
Standing in front of her own home, Melissa Mitchell is surrounded by houses where neighbors died of cancer.
This is my house.
That's the Ingrims' [house]. They both passed. One had lung cancer.
This is the Cornett's house. She passed away of liver cancer.
That is the [redacted] [house]. Their adult son who grew up was diagnosed with kidney cancer.
And the people across the street, his mother was diagnosed with breast cancer.
REUTERS/Eric Cox
BRIDGETON, MISSOURI
The 43,000 tons of radioactive waste and soil came from a top-secret initiative: The Manhattan Project, which built the atomic bombs America dropped on Japan in 1945.
In 1973, that waste ended up in an unlined landfill in Bridgeton, Missouri, a St. Louis suburb. Workers spread it to cover trash and construction debris. In 1990, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency declared the West Lake Landfill one of the nation’s most contaminated sites requiring cleanup. Still, many who lived near the dump didn’t know about West Lake’s toxic history.
It wasn’t until 2012, when garbage was burning underground, that the landfill burst fully into public view. The stench smothered nearby neighborhoods. Parents shut their kids inside. Emergency responders drew up evacuation plans, worried the smoldering waste would cause a nuclear catastrophe. Residents mobilized, spotlighting stories of children dying from cancer. And they pressed waste-management giant Republic Services, the dump’s owner, to remove the radioactive waste. In 2017, HBO aired a documentary about their cause.
Testing for radioactive material
The EPA has taken more than 1,000 soil samples from the West Lake Landfill and the surrounding area and found some radioactive material outside the site. The agency continues to investigate and says it will use the findings in deciding on a cleanup plan.
Sources: EPA, Google Earth
For all the radioactive publicity, though, Republic beat back neighbors’ claims. The nuclear waste is still there, and the government hasn’t said when a cleanup will begin.
In refuting neighbors’ complaints, Republic tapped an unlikely ally that U.S. corporations have leaned on for decades: a federal health agency set up to protect people from environmental hazards just like the West Lake dump.
A 2015 report by that small bureaucracy, the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR), did not identify any radioactive material outside the landfill. It declared that the landfill posed no health risk to the community and that radioactive gas would not leave the site. Its assessment contradicted findings from two sets of scientists: some hired by Missouri’s Attorney General and others from an environmental consulting firm working with residents. Republic still uses the ATSDR report to argue for a less expensive cleanup of the contamination, despite mounting evidence that the agency’s assessment was wrong.
Some residents told Reuters they resent the agency’s part in the drawn-out saga. Deborah Mitchell grew up in Spanish Village, less than a mile from the dump. She lost both parents to cancer and battled the disease herself. Dozens of neighbors have similar stories. Three cancer researchers told Reuters the number of cases in the neighborhood is worrisome and requires comprehensive study. That’s never been done.
“You just feel like you’re being gaslighted by your own government,” Mitchell said of the ATSDR’s role.
Republic Services, in an emailed response to Reuters questions, said it agrees with the ATSDR’s finding that the landfill poses no risk to the community. Its own experts reached a similar conclusion in 2015, it said.
The company has “always advocated for the responsible remediation of West Lake,” says the statement from Republic subsidiary Bridgeton Landfill LLC. The company has spent “tens of millions of dollars” studying the landfill and has “fully complied with every EPA directive.”
Also responsible for the site are mining firm Cotter Corp and the U.S. Department of Energy, manager of the U.S. nuclear weapons arsenal. The DOE declined to comment, and Cotter did not respond to questions about the cleanup plans.
Republic’s use of the ATSDR to argue for a less extensive cleanup of the West Lake Landfill is a strategy some companies wield at toxic sites across the U.S.
The ATSDR, part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, is a public health agency that advises the EPA. It was created in 1980 by a landmark federal law that required polluters to clean up their toxic messes. The agency was meant to safeguard the public by identifying risks from those sites. Instead, it regularly downplays and disregards neighbors’ health concerns, a Reuters investigation found. Companies and other polluters wield the agency’s work against the people it is meant to protect.
The agency issued 428 reports containing 1,582 health-related findings from 2012 to 2023. In 68% of its findings, it declared communities safe from hazards or did not make any determination at all, a Reuters review found.
ATSDR’s record of finding little harm at the nation’s most contaminated waste sites strains credulity, said Judith Enck, a former regional administrator for the EPA. She is now president and founder of Beyond Plastics, a nonprofit that seeks to end plastics pollution.
“This is not at all surprising and why I advise community groups not to request ATSDR involvement,” she said. “ATSDR has a long history of minimizing environmental health problems, and that needs an independent investigation by Congress.”
164.jpg
SEEKING ANSWERS: Tonya Mason asks a question during a May, 9, 2023, Environmental Protection Agency meeting in Bridgeton, Missouri. The meeting was about cleanup plans for a landfill holding radioactive waste. Mason fears her health problems are tied to the landfill. REUTERS/Alyssa Pointer
The agency’s frequent declarations of no harm often are rooted in faulty research, Reuters found. At least 38% of the time, agency reports show, its researchers relied on old or flawed data.
Reuters consulted with 15 sources with experience in environmental and public health for its analysis.
ATSDR officials did not respond to questions about its overall performance, errors in its work, or how polluters use its reports. In an emailed statement to Reuters, it noted that its report on the West Lake Landfill did identify one potential harm: that radioactive dust particles could be released if the surface of the landfill were disturbed. Those particles could be inhaled by workers and harm their health, the statement said.
“At the West Lake Landfill Site, ATSDR did not have evidence that residents were drinking landfill contaminated groundwater, eating or incidentally ingesting landfill contaminated soils, breathing landfill-related radon, or absorbing radiation emitted by landfill contaminants,” the statement said.
It is impossible to know how often the agency has been correct in declaring communities safe, because the search for harm often ends once the ATSDR reports its findings. Still, Reuters found at least 20 instances from 1996 to 2017 where the agency declared that a potential hazard posed no health risk – only to be refuted later by other government agencies or the ATSDR itself. Those reports relied on outdated or limited data, contained math errors or provided overly optimistic conclusions.
Patrick Breysse, who led the agency from 2014 until 2022, said that out of the hundreds of reports the ATSDR has published, 20 is a small number. And he noted that not all polluted sites are dangerous.
But he acknowledged that the agency often bases decisions on whatever information happens to be at hand rather than its own well-constructed studies.
The agency told Reuters it uses “the best available science to protect communities from harmful health effects related to exposure to hazardous substances.”
“Because ATSDR is a non-regulatory federal public health agency, typically ATSDR relies on other agencies for environmental sampling data, including regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), whose purview is to perform environmental sampling,” the agency said.
Breysse highlighted instances in which the ATSDR has intervened to help the public. Among its successes, the agency’s recommendations helped prevent increased pollution from a proposed metal-recycling plant expansion in Chicago. It also helped identify a 2016 public health crisis in Flint, Michigan, where drinking water was contaminated with high levels of lead, triggering a federal emergency.
The Reuters analysis is the most comprehensive ever conducted of the agency, which has been the target of previous probes by Congress and the Government Accountability Office. Despite decades of criticism, the agency continues to publish research that relies upon practices its own review board, in a 2010 evaluation, called “virtually useless” and “not very good.”
Some companies have seized upon the agency’s weakness. They’ve used its research to fend off lawsuits, deny victims compensation, criticize their opponents, and argue to delay, reduce or cancel cleanup of their toxic messes. ATSDR’s work has helped polluters save at least tens of millions of dollars on cleanups, delayed billions of dollars in medical claims and exposed millions of people to potential harm.
"I thought, my God, this is going to hurt one of my kids."
DAWN CHAPMAN
SINKING FEELING: Dawn Chapman co-founded Just Moms STL, a group fighting for cleanup of the West Lake Landfill, after the site’s stench overtook her home in 2013. Chapman lives about three miles from the landfill in Maryland Heights, Missouri. REUTERS/Eric Cox
In addition to Republic Services – the nation’s second-largest waste management operator – companies that have touted faulty ATSDR research include aerospace giant Boeing and Drummond Co Inc, an international coal company based in Alabama. The U.S. Navy and other government entities have benefited, too. ( See related article).
Their tactics follow a familiar corporate practice of trumpeting flawed science. The tobacco industry touted shabby research to claim cigarettes were safe. The fossil fuel industry used the strategy to call climate change a myth.
Republic began leveraging the 2015 ATSDR report about West Lake the day it was released. The trash giant had formed a group called the Coalition to Keep Us Safe to assert grassroots support for capping the radioactive waste rather than removing it. Republic says this cheaper option poses fewer potential health risks. The coalition blasted social media with the health agency’s conclusions. The coalition’s leader, Molly Teichman, taunted local activists through her personal account on Twitter, the social media platform since rebranded as X.
“Dear mombots of #westlakelandfill, your reality tv show is over," she tweeted. "Go home and hangout with your kids – they miss you."
The posts were deleted after Reuters attempted to contact Teichman, who did not respond to multiple requests for comment. Republic Services sent Reuters a written statement disassociating the company from her remarks.
“These comments were not in alignment with our views, objectives or approach,” the statement said.
Using the agency to defend polluters isn’t what lawmakers intended when they wrote the 1980 Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, commonly known as the Superfund law, said Rena Steinzor, a former congressional staff counsel who advised the law’s authors after it was enacted.
“It is a perversion,” said Steinzor, now a law professor at the University of Maryland. “I’m saddened but not shocked they’ve been subverted.”
‘Highly suggestive’ of a problem
In June 2006, Deborah Mitchell returned to her childhood home in Spanish Village to help her father after her mother, Janice Majka, died of pancreatic cancer at age 64.
Mitchell, who wasn’t feeling well herself, says she went for a run in the neighborhood and stopped to use the restroom at a hotel. What she saw there scared her. First, blood in her stool. Then a notice about an EPA meeting to discuss radioactive waste buried in the landfill.
She was shocked. Mitchell and other kids grew up playing in the dirt around Spanish Village, a hilly enclave of cul-de-sacs, carports and above-ground swimming pools. She and others talk of riding their bikes to climb a giant pile known as Sand Mountain. They swung from a vine into a creek that flowed downhill from the direction of the landfill toward their homes. At the edges of the dump, they dug for Native American beads and arrowheads. They’d be so dirty when they got home, they’d have to hose off before going inside.
Mitchell attended the EPA meeting in 2006 with her father and asked the small gathering how many had cancer. Five people raised their hands, she says. Within a year, she and her father would be among them.
In July 2006, at age 38, Mitchell was diagnosed with colorectal cancer. The following year, her father, Robert Majka, a nonsmoker, was diagnosed with lung cancer at age 68. Around the same time, Valerie Shelton, a 59-year-old who lived across the street, was diagnosed with kidney cancer.
Mitchell’s father died in 2008, Shelton in 2013. In the houses surrounding them, five other neighbors died of cancer between 2019 and 2022.
Though Mitchell’s cancer has been in remission for more than a decade, she suffers from multiple sclerosis. There is no evidence linking the autoimmune disease to environmental radiation exposure, but she and other residents worry that could be the cause. Her health problems and frequent doctor visits make it impossible for her to work full time. Once an extremely active woman and avid cyclist, she now struggles to walk.
QUESTIONS: Deborah Mitchell wonders if growing up near a landfill containing radioactive waste in Bridgeton, Missouri, caused her and her family’s cancers as well as her multiple sclerosis. Mitchell now lives in Fleming Island, Florida, where she is shown walking her dog. REUTERS/Octavio Jones
Reuters reporters tracked down current or former residents of half of the 92 homes in Spanish Village. At least 33 of those people have been diagnosed since the 1980s with cancers covered by the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act, a federal law that has compensated people exposed to nuclear waste from early atomic weapons programs. To verify the cases, reporters interviewed family members, friends and neighbors and reviewed medical records, death certificates, obituaries or social media posts.
Proving the existence of a cancer cluster is difficult, if not impossible, cancer researchers say, even when there's a glaring suspected cause such as radiation. That's because many factors are at play, including genetics, people moving in and out of areas, and duration of exposure to various carcinogens. Scientists also don’t fully understand what causes cancer.
Still, the Reuters finding of 33 cancer cases in Spanish Village is “highly suggestive” of a problem, said Sarah Chavez, a public health scientist at Washington University in St. Louis who reviewed the news organization’s research. Chavez heads the Missouri Cancer Consortium, a group that studies and tracks cancer disparities.
The health of people living near the landfill has never been comprehensively studied. In its statement to Reuters, Republic’s Bridgeton subsidiary pointed to a 2014 state review of cancer counts among current residents. It found some zip codes near the site had higher-than-expected rates of adult leukemia or childhood brain cancer. The study did not find elevated cancer rates in the zip code that includes Spanish Village. Chavez said the 2014 report covered too few illnesses and failed to track residents such as Mitchell who had moved away.
Testing of dust samples in Spanish Village homes resulted in dueling results, each the subject of criticism from opposing parties. Republic points to a 2017 EPA-funded study of dust samples from two Spanish Village homes, which reported no radiation from the landfill. But another scientist found high levels of radioactivity in at least eight Spanish Village homes. He conducted some of his testing for plaintiff’s attorneys.
Many in the community interviewed by Reuters recalled their hopes that the ATSDR would bring relief. But the agency’s 2015 report about West Lake said the community was not exposed to radiation from the dump. It did not investigate concerns about cancer and other illnesses.
In its statement to Reuters, the ATSDR said it relied on data the EPA provided in 2015 to form its conclusions about the landfill.
Earlier this year, led by Sen. Josh Hawley of Missouri, the U.S. Senate approved federal legislation that would compensate residents near the landfill as part of a $50 billion program for victims of Manhattan Project radiation. President Biden vowed to sign the bill into law if it passes the House, but Speaker Mike Johnson has not scheduled it for a vote.
“Locals have been telling the government that its studies were wrong for years,” Hawley said in an emailed response to Reuters questions. “The ATSDR’s faulty findings just underscore the blatant negligence at play here.”
‘Doubt is what they want’
The ATSDR is responsible for evaluating health hazards at Superfund sites. It is supposed to help prevent or reduce exposure to those hazards and the illnesses they can cause. The agency issues findings and makes recommendations for reducing risk, but it has no rule-making or regulatory authority.
The EPA, which does have regulatory authority, determines how much waste polluters must clean up at Superfund sites. It considers the ATSDR’s findings and recommendations when making those decisions.
The reviews have the potential to protect the health of millions of Americans. Approximately 78 million live within three miles of a Superfund site.
Toxic sites across the US
The EPA estimates approximately 78 million Americans live within three miles of a Superfund site. Taken together, the areas cover about 65,000 square miles, roughly the size of Wisconsin.
Source: EPA
From the outset, two influential industry groups became unlikely champions of the agency. The Chemical Manufacturers Association and the American Petroleum Institute joined an environmental group in a 1982 lawsuit to force the federal government to create the ATSDR. Its work, they said in court filings, was important to determine whether contaminants were making people sick.
In reality, however, studies of pollution often yield inconclusive results about risks to human health. Using that uncertainty to deflect regulation and liability is a long-standing corporate strategy, six professors who study corporate influence on public health told Reuters.
In the case of toxic waste sites, weak and inconclusive ATSDR reports give polluters authoritative, government-backed uncertainty to argue against extensive cleanups, Reuters found.
Spokespersons for the two industry groups that joined the 1982 lawsuit declined to comment on the case because it was filed so long ago.
“The last thing industry wants is an effective ATSDR that can say with more precision how dangerous these chemicals are,” said Thomas Burke, who was deputy assistant administrator of the EPA’s Office of Research and Development until 2017. Burke helped write the 1980 Superfund law and now teaches at Johns Hopkins University’s School of Public Health.
“Doubt is what they want,” Burke said.
Republic Services took exception to Burke’s assessment. “Bridgeton Landfill, LLC wants an effective ATSDR that helps the public understand who is truly exposed and who is not, and what genuine risks exist and do not exist,” a company spokesman said in an email to Reuters. “We believe ATSDR has done that at West Lake."
REUTERS VIDEO
The landfill next door
By 1993, the Washington Legal Foundation was encouraging industry to get involved in the ATSDR’s process to try to influence the agency’s health assessments. Funded by companies like Koch Industries and Philip Morris, the legal organization has filed briefs in lawsuits supporting companies like Exxon and Monsanto.
In a 1993 publication, the WLF said that tough ATSDR assessments could be costly for industry but that “early participation” in ATSDR reviews “can be highly advantageous.” The WLF noted that some reports had led to less extensive cleanups.
That same year, the foundation held an off-the-record luncheon for industry titled, "How to Minimize Superfund Liability by Successfully Handling the ATSDR Health Assessment Process.” Among the promoted speakers: Barry Johnson, then ATSDR’s assistant administrator. In recent interviews, Johnson said he does not remember the event or efforts by industry to influence the agency.
The WLF declined to comment on its earlier activities and said the ATSDR is no longer a focus for the organization.
Agency employees meet often with industry representatives while collecting information for assessments, said Burt Cooper, who retired in 2016 after 20 years as an ATSDR environmental health scientist. It was not unusual for companies or the military to pressure the agency, he said, though he could not recall specific incidents.
“You get beat up,” Cooper said. “These are high-paid attorneys, and you’re there trying to do the best you can with more meager resources.”
Despite the pressure, Cooper said agency officials never directed him to make a change in a report that wasn’t based on public health. “I was very proud of the ethics and devotion to public health that the agency had,” he said.
Outside influence
A 2008 congressional inquiry into the ATSDR’s performance found that industry and political influence was contributing to deficient research. Among the examples the committee found: The ATSDR bowed to pressure from a company executive and elected officials while studying contamination from a Brush Wellman beryllium plant in Elmore, Ohio.
The multinational company, now called Materion, is the sole U.S. producer of beryllium, a soft metal used in the aerospace, automotive and other industries. In 2006, the company was considering expanding its Elmore plant.
Beryllium is a carcinogen and can also cause lung disease. At the request of then-U.S. Sen. Mike DeWine, the ATSDR assessed air emissions from the plant in 2001 and found no health concerns. But the report's authors said more work was necessary to be sure. In 2006, the ATSDR announced plans to test blood from up to 200 people in the community to look for signs of exposure to the metal.
The company’s president and chief operating officer, Richard J. Hipple, didn’t like that plan. He wrote to DeWine and then-Governor Bob Taft.
The ATSDR’s plans “are likely to seriously damage Brush Wellman’s reputation in the Elmore community, unfairly elevate concerns about potential beryllium health effects … and increase the likelihood of litigation by plaintiff’s lawyers using the ATSDR as justification,” Hipple told DeWine in a March 2006 letter reviewed by Reuters.
After hearing from Hipple, Taft sent a handwritten note to the secretary of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Taft complained that the ATSDR’s actions could dissuade Brush Wellman from expanding the plant. “Please have someone look into this and get back to me,” Taft wrote.
Brush Wellman announced its decision to expand in Elmore in September of that year. In November, the ATSDR announced that it had tested the blood of 18 people – 91% fewer than it had planned before politicians intervened. The tests showed no major health issues linked to beryllium from the site, the agency reported.
The agency’s approach was “scaled back significantly” based partly on concerns raised by elected officials and the company, according to a 2006 ATSDR document titled "ATSDR Brush Wellman Background Paper."
Emissions at the company's Elmore plant have remained "well-below" state and federal safety regulations for decades, said Materion spokesman Jason Saragian. He said the company could not speculate about past events.
DeWine, Hipple and Taft declined to comment on the 2006 events.
Finding ‘no effect’
The Reuters review of 428 agency reports found the agency commonly cites outdated data and often lacks adequate air, water and soil samples. In 83 reports, the agency based assurances of no harm on studies, samples or equipment it admitted were flawed. This includes its West Lake Landfill report. Despite acknowledging the use of faulty equipment to collect air samples, the report said those samples showed no radiation leaving the site.
The lack of accurate and current information makes it difficult to reach definitive conclusions about health risks, more than a dozen independent scientists told Reuters.
“The methods they use and assumptions they apply often result in studies that find no effect,” said David Michaels, an epidemiologist at the George Washington University School of Public Health.
Breysse, the former ATSDR director, said the agency’s lack of adequate funding makes it a challenge to conduct more thorough studies. The agency will operate with $86 million this year and a staff of roughly 200 workers – half the number it had in 2004, federal payroll data shows. It responds to about 700 requests a year to address health risks. The companies it examines often dwarf ATSDR: Republic Services has about 42,000 employees and posted revenue of $15 billion last year.
When the agency receives resources, it can do groundbreaking work, Breysse said. He cited its work to link contaminated drinking water to cancers and other illnesses suffered by Marines and civilians who worked at the Camp Lejeune military base in North Carolina. The Camp Lejeune studies, which began in 2014, cost about $40 million, according to congressional testimony and federal contracting data. That is equal to about half the agency’s annual budget. It took an act of Congress, followed by threats from two North Carolina senators, to force the U.S. Navy to fund the work.
The agency rarely receives such support at other sites. Even with this political backing, Breysse said the Defense Department tried to dictate how to conduct studies at Camp Lejeune and insisted on seeing all findings in advance. “We had to fight to maintain our independence,” Breysse said.
The Defense Department declined to comment for this story, referring questions to the Navy. The Navy did not respond to questions about whether it tried to influence the ATSDR’s work on Camp Lejeune.
The agency’s finding meant up to 1 million former base residents and workers now have an opportunity for compensation. Still, the Camp Lejeune report came long after a flawed ATSDR report in 1997 in which the agency declared the water did not harm adults.
‘Living in a graveyard’
The Missouri Attorney General sued Republic Services in 2013, accusing the company of allowing toxic, black water to run off the landfill and emitting highly offensive odors and hazardous substances into the air. In October 2015, the ATSDR published its report declaring that radioactive material in the West Lake Landfill had not left the site and posed no significant risk to the surrounding community. Two weeks later, Republic Services filed 15 expert reports in defense of the suit. Five mentioned the ATSDR health assessment.
Two press releases on a Republic website use the ATSDR report to buttress the company’s own scientific reports that declare the landfill safe. The federal public health agency “concluded that ‘groundwater, air, and soil data do not indicate a health risk to communities surrounding West Lake Landfill,’ ” one release says.
The EPA also embraced the report. Nine days after it came out, the St. Louis Post-Dispatch published an opinion piece by the EPA’s then-regional administrator, Mark Hague.
“I want to assure you that we at the Environmental Protection Agency are committed to protecting public health from the radiological contamination buried at the West Lake Landfill,” Hague wrote. “Recently, the federal Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry completed a health consultation for EPA that confirmed there is no current offsite health risk.”
In a recent interview with Reuters, Hague said he understands the community concerns but is confident the site is being managed appropriately. “I think the EPA are working really hard to get this site remedied,” he said.
"No one told us what we were moving into."
TONYA MASON
DRIVEN OUT: Tonya Mason thought she’d found her dream home when she bought this split-level house in Bridgeton, Missouri. But the stench from garbage burning in a nearby landfill kept her family from enjoying it. She said she eventually sold the house at a loss. REUTERS/Eric Cox
Less than two weeks after publication of Hague’s opinion piece, the Missouri Department of Natural Resources, working with the EPA, found soil contaminated with radioactive material at a private business near the landfill. It had been carried there by rainwater, said Christine Jump, EPA remedial project manager for West Lake. The area was covered with rock to prevent exposure. The EPA has found other contaminated soil and groundwater near the site and says it is still assessing potential risks.
The EPA’s cleanup plan has evolved as it received results of new scientific testing, agency officials told Reuters. They said they are aware of community concerns, but based on air, soil and water testing they are confident that radioactive material in the site “as it sits today” does not pose a harm to nearby residents. Conditions at the site could change, they said. And they have not finished a health analysis of groundwater outside the landfill where they found elevated levels of radium and dioxane. The EPA classifies the solvent as a likely carcinogen. It can damage the central nervous system and kidneys.
Republic, in its responses to Reuters, said the groundwater samples appeared to contain “naturally-occurring” radium “consistent with other groundwater in the region.” EPA officials told Reuters that Republic lacks enough information to make such a claim. Ongoing testing is meant to determine if radium detected in surrounding groundwater is coming from the landfill.
"I joke sometimes that that’s what I have for breakfast is a handful of pills."
TONYA MASON
MEDICAL MYSTERY: Tonya Mason was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis about two years after selling her home near the West Lake Landfill in Bridgeton, Missouri. There is no evidence linking the autoimmune disease to radiation, but she and other residents fear the dump’s radioactive waste made them sick. REUTERS/Eric Cox
Republic says none of those tests show unsafe levels of radiation that would cause people harm. The company continues to cite scientific studies, including the 2015 ATSDR report, as evidence that there is no need for a full cleanup.
Some current and past residents nearby don’t buy it. Melissa Mitchell – unrelated to cancer patient and neighbor Deborah Mitchell – moved with her two children into a three-bedroom ranch in Bridgeton in 1994. Eight years later, she was diagnosed with Grave’s disease, a thyroid condition. Her son developed a benign tumor the size of a tennis ball on his femur in 2012. Her dog died of stomach cancer. Mitchell wonders if all of their maladies were caused by radiation exposure.
Over the years, she says, she watched as neighbors fell ill all around her – next door, across the street, catty corner to her house. In five houses on the block, 10 people had cancer.
“I felt like I was living in a graveyard,” she told Reuters.
The EPA says it is now considering a plan that would require Republic and the other responsible parties to remove 94,200 cubic yards of radioactive-contaminated waste. That’s enough to fill 82 Boeing 747s.
Thirty-four years after the landfill’s designation as a Superfund site and more than eight years after the ATSDR published its report, the waste remains and trash continues to smolder underground. Because more off-site contamination has been uncovered, EPA administrators told Reuters they don’t know when the cleanup will begin. They say they hope it will be in the next decade.
How Reuters identified weaknesses in a US health agency’s work
By BENJAMIN LESSER, M.B. PELL and JAIMI DOWDELL
It is a little-known federal health agency with an unfamiliar name: the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Congress conceived it as part of the 1980 Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, commonly known as the Superfund law, meant to hold polluters responsible for the nation’s most toxic messes.
The law requires the agency to identify potential health risks at such sites to protect the people living and working around them. Reuters reporters had encountered several examples of the ATSDR failing its mission and decided to take a closer look.
To assess the agency’s work, they reviewed 428 health reports published on its website between 2012 and 2023. Those reports contained 1,582 conclusions regarding potential harms at Superfund sites or other concerns brought to the agency by communities or government agencies.
The agency often produces the reports in partnership with state agencies.
Reporters examined the ATSDR risk classification listed for each finding and categorized the conclusion: harm or potential harm found, no harm or no potential harm found, inconclusive findings. A handful of findings could not be categorized.
Fifteen people with expertise in environmental and public health vetted the Reuters methodology. They included former ATSDR employees, and state environmental health officials, academic researchers and community health advocates.
The data collected from the reports, available for download here, enabled the reporters to document:
How frequently the agency declared potential health hazards, found no hazard or failed to issue a conclusive finding.
How often the authors used outdated data to support their findings.
Reports in which the authors detailed serious limitations in the data or analysis that undermined their conclusions.
Reporters flagged reports for using outdated data when conclusions relied on data that was at least four years old. No federal standard exists for how fresh data must be to support health assessments like those the ATSDR produces. But generally, relying on data four years old or older would result in questionable findings, five public health and environmental regulatory specialists told Reuters.
WorkWeek looks at the anniversary of the bombing of Hiroshima on August 6.
A rally was held in front of the Japanese consulate in San Francisco to protest the continued militarization of Japan and Asia.
Despite Japanese constitution Article 9 which forbids offensive war the Kishida government and the previous Abe government have expanded the military and supported continued US military bases in Okinawa that the people are opposing.
WorkWeek also looks at the continued contamination of the people and workers of East Palestine,Ohio from a derailment last February 2023 by Norfolk Southern is bringing anger and frustration. The company ignited tank cars containing vinyl chloride despite the owner of the toxin sayin that they should not blow up the chemical.
According to Jame Rae Wallace who was the past president of Cleveland State University SEIU 1199 and a resident they were lied to by the company and the EPA about the danger of the toxin and are now being coerced to support a settlement agreement and class action that will not provide healthcare benefits and compensation for their homes to move out of the contaminated town.
WorkWeek looks at the growth of a fascist movement in the US and what that means for
unions and workers in the US.
WorkWeek interviews Cliff Smith who is the business manager of Roofers Local 36 in Los
Angeles. Trump and his supporters have already said that they will not accept an election
unless they win it and they have already organized an attempted coup and insurrection.
Smith and his local is planning a meeting in Los Angeles on September 7th to discuss
the rise of fascism, democracy and the formation of a workers party.
WorkWeek On Slave Labor & Free Labor In The Golden State With Professor Jean Pfealzer
https://soundcloud.com/workweek-radio/ww-8-15-24-slave-labor-free-labor-in-the-golden-state-with-professorjean-pfealzer
WorkWeek hears a presentation by Jean Pfealzer, a professor and author of California A Slave State on slave labor and free labor in California . She discussed the history of slavery in California from the Spaniards and the Missions to the Russians and then slavery when California became a state..
This presentation was part of Laborfest which commemorates the San Francisco general strike and it was held at the Angel Island immigration station where tens of thousands of immigrants including many Chinese arrived in the United States.Pfealzer besides the author of California A Slave State is also author of Driven Out:The Forgotten War Against Chinese Americans.
Additional Media:
California A Slave State With Jean Pfaelzer
https://youtu.be/JjMisZzA-n0
The History Of Slavery In California With Professor Jean Pfealzer
https://youtu.be/tfgQU0qig6Y
Additional Info:
https://www.jeanpfaelzer.com
https://soundcloud.com/workweek-radio
workweeknow [at] gmail.com
#laborradionetwork #LaborRadioPod #1u #UnionStrong
Hidden Report Reveals How Workers Got Sick While Cleaning Ohio Derailment Site
https://time.com/7011096/workers-sick-cleaning-ohio-derailment-site/
Debris from a Norfolk Southern freight train lies scattered and burning along the tracks, Feb. 4, 2023, the day after it derailed in East Palestine, Ohio. Gene J. Puskar—AP
BY ASSOCIATED PRESSAUGUST 14, 2024 3:31 PM EDT
The creeks around East Palestine, Ohio, were so badly contaminated by last year's disastrous Norfolk Southern derailment that some workers became sick during the cleanup.
Workers who reported headaches and nausea — while shooting compressed air into the creek bed, which releases chemicals from the sediment and water — were sent back to their hotels to rest, according to a report obtained by The Associated Press about their illnesses.
The findings were not released to the public last spring, despite residents' concerns about the potential health effects of exposure to the long list of chemicals that spilled and burned after the disaster. The workers' symptoms, as described in the report, are consistent with what Centers for Disease Control and Prevention workers going door-to-door in town had reported shortly after the Feb. 3, 2023, derailment.
Read more: East Palestine, One Year After Train Derailment
Since then some residents have also reported unexplained rashes, asthma and other respiratory problems, and serious diseases including male breast cancer.
Researchers are still determining how many of those health problems can be linked to the derailment and how the disaster will impact the long-term health of residents in the area near the Ohio-Pennsylvania border. Many wonder whether there will be cancer clusters down the road, which of course won't be clear for years.
In the meantime, residents have until Aug. 22 to decide whether to accept up to $25,000 — as part of a $600 million class action settlement with the railroad to compensate them for any future health problems. Accepting that money though means giving up the right to sue later, when the cost of health care coverage and specific treatments needed will become more clear.
Norfolk Southern spokesperson Heather Garcia said none of the workers who got sick during the cleanup “reported lingering or long-term symptoms."
“The health and safety of our employees, contractors, and the community has been paramount throughout the recovery in East Palestine,” Garcia said.
The creek cleanup work continued, but nearly three weeks later, another worker got sick. This time, it was halted altogether. While there've been other cleanup projects since then, they've stopped using high-pressure air knife tools.
Independent toxicologist George Thompson who has been following the aftermath of the Ohio wreck said the cleanup contractors, overseen by the Environmental Protection Agency, should have known the work they were doing would release chemicals from the sediment into the air and water. In fact, that is what CTEH was monitoring while the project was underway. And with one of the main streams, Sulphur Run, going directly through town and in culverts under homes and offices, Thompson said those chemicals could have infiltrated buildings.
“You’re just spreading out the chemicals for exposure,” Thompson said. “And I just think that it was not an informed decision to use air knifing at all.”
Resident Jami Wallace said she lost her voice for two weeks after she got too close to one of the air knifing machines, which was placed near her driveway. She said when the machine was turned on, it felt like being hit by an invisible wall emitting a sweet chemical smell much like when the train derailed.
The report from CTEH was submitted to Unified Command, the group overseeing disaster response — which included federal, state and local officials along with Norfolk Southern — but no one released it despite significant public interest. CTEH's principal toxicologist Paul Nony confirmed the report was given to the command center, and officials there were alerted about the illnesses.
When CDC workers got sick — also with headaches and nausea — it generated headlines nationwide.
East Palestine resident Misti Allison said not enough is being done to monitor long-term health effects on the community, and this report substantiates their health concerns. She said this report should have never been kept from the public.
“It’s absolutely egregious, and that shouldn’t happen. I think that any type of information like that — just like when the CDC workers came to the area and got sick — that should be disclosed instead of diminished,” Allison said. “Especially when it comes to human health, nothing should be swept under the rug.”
The East Palestine derailment that happened on the night of Feb. 3, 2023, was easily the worst rail disaster since a crude oil train leveled the small Canadian town of Lac Megantic and killed 47 people in 2013. It prompted a national reckoning with rail safety and calls for reform — although proposals for new industry rules have stalled in Congress.
Thirty-eight cars derailed, including 11 carrying hazardous materials such as butyl acrylate and vinyl chloride. After the crash, a fire burned for days. Fearing the five vinyl chloride cars would explode, officials then needlessly blew them open, and intentionally burned the toxic plastic ingredient.
That created a massive plume of thick black smoke over the area. The NTSB determined that the decision-makers that day never received the key opinion — that the cars were not likely to explode — from the chemical manufacturer.
The major freight railroads responded by pledging to add hundreds more trackside detectors nationwide to help spot mechanical problems. They also reevaluated the way they respond to alerts and even before alerts, the way they track rising temperatures from an overheating wheel bearing.
This summer’s completion of the NTSB investigation into the crash brought renewed hope that Congress might pass a rail safety bill, but little action has been taken outside of a House hearing on the subject last month.
CTEH said that its environmental testing around the creeks confirmed there were elevated levels of an assortment of chemicals in the air and sediment. Still, the group didn't find either of the two chemicals of greatest concern: vinyl chloride or butyl acrylate. Sediment testing at nine locations along the creeks where cleanup workers reported strong odors did show 37 different chemical compounds that were primarily either hydrocarbons or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Because of that, CTEH said it was clear that some of the contamination in the creeks came from industries that operated in the area years before the 2023 derailment. Still, those compounds could have also been created from chemicals burning after the train crash.
Nony, the head CTEH toxicologist, said that his company's responsibility during the air knifing operation was primarily to monitor air quality.
The EPA has said that it doesn't believe people are being exposed to any toxic chemicals on an ongoing basis because concerning levels of chemicals haven't been found in their air and water tests since the evacuation order was lifted.
In follow-up testing this year, the agency did find small amounts of vinyl chloride and other chemicals at the crash site, but citing only small amounts and the fact that the contaminated soil was removed, the agency said they don't represent a risk to human health.
The overall clean up effort in East Palestine is expected to be completed sometime later this year.
How a US health agency became a shield for polluters
https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/usa-pollution-atsdr-landfill/
How a US health agency became a shield for polluters
Companies and others responsible for some of America's most toxic waste sites are using a federal health agency’s faulty reports to save money on cleanups, defend against lawsuits and deny victims compensation, a Reuters investigation found. A Missouri neighborhood's tale.
By JAIMI DOWDELL, M.B. PELL, BENJAMIN LESSER, MICHELLE CONLIN, PHOEBE QUINTON and WAYLON CUNNINGHAMFiled Aug. 7, 2024, 11 a.m. GMT
William Wright
Non-Hodgkins lymphoma
Jean Nowlin
Breast cancer
Kathleen Schindler
Breast cancer
Melanie Sue Herberger
Lung cancer
Mary Patricia Sanguinet
Breast cancer
Martha Kowalczyk
Breast and lung cancer
Kathleen Ann Laube
Breast cancer
Donald Wagner
Pancreatic and prostate cancer
Mark Tinker
Brain cancer
Valerie Shelton
Kidney cancer
Janice Majka
Pancreatic cancer
Robert Majka
Lung cancer
Deborah Mitchell
Colorectal cancer
Fred Ingrim
Lung cancer
Arthur "Rex" Cornett
Lymphoma
Joan Cornett
Breast and liver cancer
Becky (Baum) Davis
Breast cancer
Julie Renee (Baum) Glenn
Breast cancer
Thomas Baum
Lung cancer
Diana Baum
Breast cancer
Charles Stafford
Colon cancer
Harold Krueger
Pancreatic cancer
Evelyn Krueger
Esophogeal cancer
Martha Wilson
Lung and bladder cancer
John Elton James
Esophogeal cancer
JoAnn Arter
Lung cancer
Michelle Herbel
Cervical cancer
Deborah Ann Berry
Pancreatic cancer
Linda Calvo
Bladder cancer
Patricia "PattytheK" Bott
Breast cancer
Dennis Hoppe
Stomach, esophogeal, liver and lung cancer
Carroll Edward Johns
Colon cancer
Deborah Jane Winston
Kidney cancer
Westlake Landfill
Spanish Village
When they bought their homes in the Spanish Village neighborhood northwest of St. Louis, many residents had no idea a radioactive landfill sat less than a mile away.
Health conditions mounted over the years, suggesting something wasn’t right.
Reuters reporters tracked down current or former residents of half of the neighborhood’s 92 homes. At least 33 of those people have been diagnosed since the 1980s with types of cancer that have been linked to radiation.
Standing in front of her own home, Melissa Mitchell is surrounded by houses where neighbors died of cancer.
This is my house.
That's the Ingrims' [house]. They both passed. One had lung cancer.
This is the Cornett's house. She passed away of liver cancer.
That is the [redacted] [house]. Their adult son who grew up was diagnosed with kidney cancer.
And the people across the street, his mother was diagnosed with breast cancer.
REUTERS/Eric Cox
BRIDGETON, MISSOURI
The 43,000 tons of radioactive waste and soil came from a top-secret initiative: The Manhattan Project, which built the atomic bombs America dropped on Japan in 1945.
In 1973, that waste ended up in an unlined landfill in Bridgeton, Missouri, a St. Louis suburb. Workers spread it to cover trash and construction debris. In 1990, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency declared the West Lake Landfill one of the nation’s most contaminated sites requiring cleanup. Still, many who lived near the dump didn’t know about West Lake’s toxic history.
It wasn’t until 2012, when garbage was burning underground, that the landfill burst fully into public view. The stench smothered nearby neighborhoods. Parents shut their kids inside. Emergency responders drew up evacuation plans, worried the smoldering waste would cause a nuclear catastrophe. Residents mobilized, spotlighting stories of children dying from cancer. And they pressed waste-management giant Republic Services, the dump’s owner, to remove the radioactive waste. In 2017, HBO aired a documentary about their cause.
Testing for radioactive material
The EPA has taken more than 1,000 soil samples from the West Lake Landfill and the surrounding area and found some radioactive material outside the site. The agency continues to investigate and says it will use the findings in deciding on a cleanup plan.
Sources: EPA, Google Earth
For all the radioactive publicity, though, Republic beat back neighbors’ claims. The nuclear waste is still there, and the government hasn’t said when a cleanup will begin.
In refuting neighbors’ complaints, Republic tapped an unlikely ally that U.S. corporations have leaned on for decades: a federal health agency set up to protect people from environmental hazards just like the West Lake dump.
A 2015 report by that small bureaucracy, the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR), did not identify any radioactive material outside the landfill. It declared that the landfill posed no health risk to the community and that radioactive gas would not leave the site. Its assessment contradicted findings from two sets of scientists: some hired by Missouri’s Attorney General and others from an environmental consulting firm working with residents. Republic still uses the ATSDR report to argue for a less expensive cleanup of the contamination, despite mounting evidence that the agency’s assessment was wrong.
Some residents told Reuters they resent the agency’s part in the drawn-out saga. Deborah Mitchell grew up in Spanish Village, less than a mile from the dump. She lost both parents to cancer and battled the disease herself. Dozens of neighbors have similar stories. Three cancer researchers told Reuters the number of cases in the neighborhood is worrisome and requires comprehensive study. That’s never been done.
“You just feel like you’re being gaslighted by your own government,” Mitchell said of the ATSDR’s role.
Republic Services, in an emailed response to Reuters questions, said it agrees with the ATSDR’s finding that the landfill poses no risk to the community. Its own experts reached a similar conclusion in 2015, it said.
The company has “always advocated for the responsible remediation of West Lake,” says the statement from Republic subsidiary Bridgeton Landfill LLC. The company has spent “tens of millions of dollars” studying the landfill and has “fully complied with every EPA directive.”
Also responsible for the site are mining firm Cotter Corp and the U.S. Department of Energy, manager of the U.S. nuclear weapons arsenal. The DOE declined to comment, and Cotter did not respond to questions about the cleanup plans.
Republic’s use of the ATSDR to argue for a less extensive cleanup of the West Lake Landfill is a strategy some companies wield at toxic sites across the U.S.
The ATSDR, part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, is a public health agency that advises the EPA. It was created in 1980 by a landmark federal law that required polluters to clean up their toxic messes. The agency was meant to safeguard the public by identifying risks from those sites. Instead, it regularly downplays and disregards neighbors’ health concerns, a Reuters investigation found. Companies and other polluters wield the agency’s work against the people it is meant to protect.
The agency issued 428 reports containing 1,582 health-related findings from 2012 to 2023. In 68% of its findings, it declared communities safe from hazards or did not make any determination at all, a Reuters review found.
ATSDR’s record of finding little harm at the nation’s most contaminated waste sites strains credulity, said Judith Enck, a former regional administrator for the EPA. She is now president and founder of Beyond Plastics, a nonprofit that seeks to end plastics pollution.
“This is not at all surprising and why I advise community groups not to request ATSDR involvement,” she said. “ATSDR has a long history of minimizing environmental health problems, and that needs an independent investigation by Congress.”
164.jpg
SEEKING ANSWERS: Tonya Mason asks a question during a May, 9, 2023, Environmental Protection Agency meeting in Bridgeton, Missouri. The meeting was about cleanup plans for a landfill holding radioactive waste. Mason fears her health problems are tied to the landfill. REUTERS/Alyssa Pointer
The agency’s frequent declarations of no harm often are rooted in faulty research, Reuters found. At least 38% of the time, agency reports show, its researchers relied on old or flawed data.
Reuters consulted with 15 sources with experience in environmental and public health for its analysis.
ATSDR officials did not respond to questions about its overall performance, errors in its work, or how polluters use its reports. In an emailed statement to Reuters, it noted that its report on the West Lake Landfill did identify one potential harm: that radioactive dust particles could be released if the surface of the landfill were disturbed. Those particles could be inhaled by workers and harm their health, the statement said.
“At the West Lake Landfill Site, ATSDR did not have evidence that residents were drinking landfill contaminated groundwater, eating or incidentally ingesting landfill contaminated soils, breathing landfill-related radon, or absorbing radiation emitted by landfill contaminants,” the statement said.
It is impossible to know how often the agency has been correct in declaring communities safe, because the search for harm often ends once the ATSDR reports its findings. Still, Reuters found at least 20 instances from 1996 to 2017 where the agency declared that a potential hazard posed no health risk – only to be refuted later by other government agencies or the ATSDR itself. Those reports relied on outdated or limited data, contained math errors or provided overly optimistic conclusions.
Patrick Breysse, who led the agency from 2014 until 2022, said that out of the hundreds of reports the ATSDR has published, 20 is a small number. And he noted that not all polluted sites are dangerous.
But he acknowledged that the agency often bases decisions on whatever information happens to be at hand rather than its own well-constructed studies.
The agency told Reuters it uses “the best available science to protect communities from harmful health effects related to exposure to hazardous substances.”
“Because ATSDR is a non-regulatory federal public health agency, typically ATSDR relies on other agencies for environmental sampling data, including regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), whose purview is to perform environmental sampling,” the agency said.
Breysse highlighted instances in which the ATSDR has intervened to help the public. Among its successes, the agency’s recommendations helped prevent increased pollution from a proposed metal-recycling plant expansion in Chicago. It also helped identify a 2016 public health crisis in Flint, Michigan, where drinking water was contaminated with high levels of lead, triggering a federal emergency.
The Reuters analysis is the most comprehensive ever conducted of the agency, which has been the target of previous probes by Congress and the Government Accountability Office. Despite decades of criticism, the agency continues to publish research that relies upon practices its own review board, in a 2010 evaluation, called “virtually useless” and “not very good.”
Some companies have seized upon the agency’s weakness. They’ve used its research to fend off lawsuits, deny victims compensation, criticize their opponents, and argue to delay, reduce or cancel cleanup of their toxic messes. ATSDR’s work has helped polluters save at least tens of millions of dollars on cleanups, delayed billions of dollars in medical claims and exposed millions of people to potential harm.
"I thought, my God, this is going to hurt one of my kids."
DAWN CHAPMAN
SINKING FEELING: Dawn Chapman co-founded Just Moms STL, a group fighting for cleanup of the West Lake Landfill, after the site’s stench overtook her home in 2013. Chapman lives about three miles from the landfill in Maryland Heights, Missouri. REUTERS/Eric Cox
In addition to Republic Services – the nation’s second-largest waste management operator – companies that have touted faulty ATSDR research include aerospace giant Boeing and Drummond Co Inc, an international coal company based in Alabama. The U.S. Navy and other government entities have benefited, too. ( See related article).
Their tactics follow a familiar corporate practice of trumpeting flawed science. The tobacco industry touted shabby research to claim cigarettes were safe. The fossil fuel industry used the strategy to call climate change a myth.
Republic began leveraging the 2015 ATSDR report about West Lake the day it was released. The trash giant had formed a group called the Coalition to Keep Us Safe to assert grassroots support for capping the radioactive waste rather than removing it. Republic says this cheaper option poses fewer potential health risks. The coalition blasted social media with the health agency’s conclusions. The coalition’s leader, Molly Teichman, taunted local activists through her personal account on Twitter, the social media platform since rebranded as X.
“Dear mombots of #westlakelandfill, your reality tv show is over," she tweeted. "Go home and hangout with your kids – they miss you."
The posts were deleted after Reuters attempted to contact Teichman, who did not respond to multiple requests for comment. Republic Services sent Reuters a written statement disassociating the company from her remarks.
“These comments were not in alignment with our views, objectives or approach,” the statement said.
Using the agency to defend polluters isn’t what lawmakers intended when they wrote the 1980 Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, commonly known as the Superfund law, said Rena Steinzor, a former congressional staff counsel who advised the law’s authors after it was enacted.
“It is a perversion,” said Steinzor, now a law professor at the University of Maryland. “I’m saddened but not shocked they’ve been subverted.”
‘Highly suggestive’ of a problem
In June 2006, Deborah Mitchell returned to her childhood home in Spanish Village to help her father after her mother, Janice Majka, died of pancreatic cancer at age 64.
Mitchell, who wasn’t feeling well herself, says she went for a run in the neighborhood and stopped to use the restroom at a hotel. What she saw there scared her. First, blood in her stool. Then a notice about an EPA meeting to discuss radioactive waste buried in the landfill.
She was shocked. Mitchell and other kids grew up playing in the dirt around Spanish Village, a hilly enclave of cul-de-sacs, carports and above-ground swimming pools. She and others talk of riding their bikes to climb a giant pile known as Sand Mountain. They swung from a vine into a creek that flowed downhill from the direction of the landfill toward their homes. At the edges of the dump, they dug for Native American beads and arrowheads. They’d be so dirty when they got home, they’d have to hose off before going inside.
Mitchell attended the EPA meeting in 2006 with her father and asked the small gathering how many had cancer. Five people raised their hands, she says. Within a year, she and her father would be among them.
In July 2006, at age 38, Mitchell was diagnosed with colorectal cancer. The following year, her father, Robert Majka, a nonsmoker, was diagnosed with lung cancer at age 68. Around the same time, Valerie Shelton, a 59-year-old who lived across the street, was diagnosed with kidney cancer.
Mitchell’s father died in 2008, Shelton in 2013. In the houses surrounding them, five other neighbors died of cancer between 2019 and 2022.
Though Mitchell’s cancer has been in remission for more than a decade, she suffers from multiple sclerosis. There is no evidence linking the autoimmune disease to environmental radiation exposure, but she and other residents worry that could be the cause. Her health problems and frequent doctor visits make it impossible for her to work full time. Once an extremely active woman and avid cyclist, she now struggles to walk.
QUESTIONS: Deborah Mitchell wonders if growing up near a landfill containing radioactive waste in Bridgeton, Missouri, caused her and her family’s cancers as well as her multiple sclerosis. Mitchell now lives in Fleming Island, Florida, where she is shown walking her dog. REUTERS/Octavio Jones
Reuters reporters tracked down current or former residents of half of the 92 homes in Spanish Village. At least 33 of those people have been diagnosed since the 1980s with cancers covered by the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act, a federal law that has compensated people exposed to nuclear waste from early atomic weapons programs. To verify the cases, reporters interviewed family members, friends and neighbors and reviewed medical records, death certificates, obituaries or social media posts.
Proving the existence of a cancer cluster is difficult, if not impossible, cancer researchers say, even when there's a glaring suspected cause such as radiation. That's because many factors are at play, including genetics, people moving in and out of areas, and duration of exposure to various carcinogens. Scientists also don’t fully understand what causes cancer.
Still, the Reuters finding of 33 cancer cases in Spanish Village is “highly suggestive” of a problem, said Sarah Chavez, a public health scientist at Washington University in St. Louis who reviewed the news organization’s research. Chavez heads the Missouri Cancer Consortium, a group that studies and tracks cancer disparities.
The health of people living near the landfill has never been comprehensively studied. In its statement to Reuters, Republic’s Bridgeton subsidiary pointed to a 2014 state review of cancer counts among current residents. It found some zip codes near the site had higher-than-expected rates of adult leukemia or childhood brain cancer. The study did not find elevated cancer rates in the zip code that includes Spanish Village. Chavez said the 2014 report covered too few illnesses and failed to track residents such as Mitchell who had moved away.
Testing of dust samples in Spanish Village homes resulted in dueling results, each the subject of criticism from opposing parties. Republic points to a 2017 EPA-funded study of dust samples from two Spanish Village homes, which reported no radiation from the landfill. But another scientist found high levels of radioactivity in at least eight Spanish Village homes. He conducted some of his testing for plaintiff’s attorneys.
Many in the community interviewed by Reuters recalled their hopes that the ATSDR would bring relief. But the agency’s 2015 report about West Lake said the community was not exposed to radiation from the dump. It did not investigate concerns about cancer and other illnesses.
In its statement to Reuters, the ATSDR said it relied on data the EPA provided in 2015 to form its conclusions about the landfill.
Earlier this year, led by Sen. Josh Hawley of Missouri, the U.S. Senate approved federal legislation that would compensate residents near the landfill as part of a $50 billion program for victims of Manhattan Project radiation. President Biden vowed to sign the bill into law if it passes the House, but Speaker Mike Johnson has not scheduled it for a vote.
“Locals have been telling the government that its studies were wrong for years,” Hawley said in an emailed response to Reuters questions. “The ATSDR’s faulty findings just underscore the blatant negligence at play here.”
‘Doubt is what they want’
The ATSDR is responsible for evaluating health hazards at Superfund sites. It is supposed to help prevent or reduce exposure to those hazards and the illnesses they can cause. The agency issues findings and makes recommendations for reducing risk, but it has no rule-making or regulatory authority.
The EPA, which does have regulatory authority, determines how much waste polluters must clean up at Superfund sites. It considers the ATSDR’s findings and recommendations when making those decisions.
The reviews have the potential to protect the health of millions of Americans. Approximately 78 million live within three miles of a Superfund site.
Toxic sites across the US
The EPA estimates approximately 78 million Americans live within three miles of a Superfund site. Taken together, the areas cover about 65,000 square miles, roughly the size of Wisconsin.
Source: EPA
From the outset, two influential industry groups became unlikely champions of the agency. The Chemical Manufacturers Association and the American Petroleum Institute joined an environmental group in a 1982 lawsuit to force the federal government to create the ATSDR. Its work, they said in court filings, was important to determine whether contaminants were making people sick.
In reality, however, studies of pollution often yield inconclusive results about risks to human health. Using that uncertainty to deflect regulation and liability is a long-standing corporate strategy, six professors who study corporate influence on public health told Reuters.
In the case of toxic waste sites, weak and inconclusive ATSDR reports give polluters authoritative, government-backed uncertainty to argue against extensive cleanups, Reuters found.
Spokespersons for the two industry groups that joined the 1982 lawsuit declined to comment on the case because it was filed so long ago.
“The last thing industry wants is an effective ATSDR that can say with more precision how dangerous these chemicals are,” said Thomas Burke, who was deputy assistant administrator of the EPA’s Office of Research and Development until 2017. Burke helped write the 1980 Superfund law and now teaches at Johns Hopkins University’s School of Public Health.
“Doubt is what they want,” Burke said.
Republic Services took exception to Burke’s assessment. “Bridgeton Landfill, LLC wants an effective ATSDR that helps the public understand who is truly exposed and who is not, and what genuine risks exist and do not exist,” a company spokesman said in an email to Reuters. “We believe ATSDR has done that at West Lake."
REUTERS VIDEO
The landfill next door
By 1993, the Washington Legal Foundation was encouraging industry to get involved in the ATSDR’s process to try to influence the agency’s health assessments. Funded by companies like Koch Industries and Philip Morris, the legal organization has filed briefs in lawsuits supporting companies like Exxon and Monsanto.
In a 1993 publication, the WLF said that tough ATSDR assessments could be costly for industry but that “early participation” in ATSDR reviews “can be highly advantageous.” The WLF noted that some reports had led to less extensive cleanups.
That same year, the foundation held an off-the-record luncheon for industry titled, "How to Minimize Superfund Liability by Successfully Handling the ATSDR Health Assessment Process.” Among the promoted speakers: Barry Johnson, then ATSDR’s assistant administrator. In recent interviews, Johnson said he does not remember the event or efforts by industry to influence the agency.
The WLF declined to comment on its earlier activities and said the ATSDR is no longer a focus for the organization.
Agency employees meet often with industry representatives while collecting information for assessments, said Burt Cooper, who retired in 2016 after 20 years as an ATSDR environmental health scientist. It was not unusual for companies or the military to pressure the agency, he said, though he could not recall specific incidents.
“You get beat up,” Cooper said. “These are high-paid attorneys, and you’re there trying to do the best you can with more meager resources.”
Despite the pressure, Cooper said agency officials never directed him to make a change in a report that wasn’t based on public health. “I was very proud of the ethics and devotion to public health that the agency had,” he said.
Outside influence
A 2008 congressional inquiry into the ATSDR’s performance found that industry and political influence was contributing to deficient research. Among the examples the committee found: The ATSDR bowed to pressure from a company executive and elected officials while studying contamination from a Brush Wellman beryllium plant in Elmore, Ohio.
The multinational company, now called Materion, is the sole U.S. producer of beryllium, a soft metal used in the aerospace, automotive and other industries. In 2006, the company was considering expanding its Elmore plant.
Beryllium is a carcinogen and can also cause lung disease. At the request of then-U.S. Sen. Mike DeWine, the ATSDR assessed air emissions from the plant in 2001 and found no health concerns. But the report's authors said more work was necessary to be sure. In 2006, the ATSDR announced plans to test blood from up to 200 people in the community to look for signs of exposure to the metal.
The company’s president and chief operating officer, Richard J. Hipple, didn’t like that plan. He wrote to DeWine and then-Governor Bob Taft.
The ATSDR’s plans “are likely to seriously damage Brush Wellman’s reputation in the Elmore community, unfairly elevate concerns about potential beryllium health effects … and increase the likelihood of litigation by plaintiff’s lawyers using the ATSDR as justification,” Hipple told DeWine in a March 2006 letter reviewed by Reuters.
After hearing from Hipple, Taft sent a handwritten note to the secretary of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Taft complained that the ATSDR’s actions could dissuade Brush Wellman from expanding the plant. “Please have someone look into this and get back to me,” Taft wrote.
Brush Wellman announced its decision to expand in Elmore in September of that year. In November, the ATSDR announced that it had tested the blood of 18 people – 91% fewer than it had planned before politicians intervened. The tests showed no major health issues linked to beryllium from the site, the agency reported.
The agency’s approach was “scaled back significantly” based partly on concerns raised by elected officials and the company, according to a 2006 ATSDR document titled "ATSDR Brush Wellman Background Paper."
Emissions at the company's Elmore plant have remained "well-below" state and federal safety regulations for decades, said Materion spokesman Jason Saragian. He said the company could not speculate about past events.
DeWine, Hipple and Taft declined to comment on the 2006 events.
Finding ‘no effect’
The Reuters review of 428 agency reports found the agency commonly cites outdated data and often lacks adequate air, water and soil samples. In 83 reports, the agency based assurances of no harm on studies, samples or equipment it admitted were flawed. This includes its West Lake Landfill report. Despite acknowledging the use of faulty equipment to collect air samples, the report said those samples showed no radiation leaving the site.
The lack of accurate and current information makes it difficult to reach definitive conclusions about health risks, more than a dozen independent scientists told Reuters.
“The methods they use and assumptions they apply often result in studies that find no effect,” said David Michaels, an epidemiologist at the George Washington University School of Public Health.
Breysse, the former ATSDR director, said the agency’s lack of adequate funding makes it a challenge to conduct more thorough studies. The agency will operate with $86 million this year and a staff of roughly 200 workers – half the number it had in 2004, federal payroll data shows. It responds to about 700 requests a year to address health risks. The companies it examines often dwarf ATSDR: Republic Services has about 42,000 employees and posted revenue of $15 billion last year.
When the agency receives resources, it can do groundbreaking work, Breysse said. He cited its work to link contaminated drinking water to cancers and other illnesses suffered by Marines and civilians who worked at the Camp Lejeune military base in North Carolina. The Camp Lejeune studies, which began in 2014, cost about $40 million, according to congressional testimony and federal contracting data. That is equal to about half the agency’s annual budget. It took an act of Congress, followed by threats from two North Carolina senators, to force the U.S. Navy to fund the work.
The agency rarely receives such support at other sites. Even with this political backing, Breysse said the Defense Department tried to dictate how to conduct studies at Camp Lejeune and insisted on seeing all findings in advance. “We had to fight to maintain our independence,” Breysse said.
The Defense Department declined to comment for this story, referring questions to the Navy. The Navy did not respond to questions about whether it tried to influence the ATSDR’s work on Camp Lejeune.
The agency’s finding meant up to 1 million former base residents and workers now have an opportunity for compensation. Still, the Camp Lejeune report came long after a flawed ATSDR report in 1997 in which the agency declared the water did not harm adults.
‘Living in a graveyard’
The Missouri Attorney General sued Republic Services in 2013, accusing the company of allowing toxic, black water to run off the landfill and emitting highly offensive odors and hazardous substances into the air. In October 2015, the ATSDR published its report declaring that radioactive material in the West Lake Landfill had not left the site and posed no significant risk to the surrounding community. Two weeks later, Republic Services filed 15 expert reports in defense of the suit. Five mentioned the ATSDR health assessment.
Two press releases on a Republic website use the ATSDR report to buttress the company’s own scientific reports that declare the landfill safe. The federal public health agency “concluded that ‘groundwater, air, and soil data do not indicate a health risk to communities surrounding West Lake Landfill,’ ” one release says.
The EPA also embraced the report. Nine days after it came out, the St. Louis Post-Dispatch published an opinion piece by the EPA’s then-regional administrator, Mark Hague.
“I want to assure you that we at the Environmental Protection Agency are committed to protecting public health from the radiological contamination buried at the West Lake Landfill,” Hague wrote. “Recently, the federal Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry completed a health consultation for EPA that confirmed there is no current offsite health risk.”
In a recent interview with Reuters, Hague said he understands the community concerns but is confident the site is being managed appropriately. “I think the EPA are working really hard to get this site remedied,” he said.
"No one told us what we were moving into."
TONYA MASON
DRIVEN OUT: Tonya Mason thought she’d found her dream home when she bought this split-level house in Bridgeton, Missouri. But the stench from garbage burning in a nearby landfill kept her family from enjoying it. She said she eventually sold the house at a loss. REUTERS/Eric Cox
Less than two weeks after publication of Hague’s opinion piece, the Missouri Department of Natural Resources, working with the EPA, found soil contaminated with radioactive material at a private business near the landfill. It had been carried there by rainwater, said Christine Jump, EPA remedial project manager for West Lake. The area was covered with rock to prevent exposure. The EPA has found other contaminated soil and groundwater near the site and says it is still assessing potential risks.
The EPA’s cleanup plan has evolved as it received results of new scientific testing, agency officials told Reuters. They said they are aware of community concerns, but based on air, soil and water testing they are confident that radioactive material in the site “as it sits today” does not pose a harm to nearby residents. Conditions at the site could change, they said. And they have not finished a health analysis of groundwater outside the landfill where they found elevated levels of radium and dioxane. The EPA classifies the solvent as a likely carcinogen. It can damage the central nervous system and kidneys.
Republic, in its responses to Reuters, said the groundwater samples appeared to contain “naturally-occurring” radium “consistent with other groundwater in the region.” EPA officials told Reuters that Republic lacks enough information to make such a claim. Ongoing testing is meant to determine if radium detected in surrounding groundwater is coming from the landfill.
"I joke sometimes that that’s what I have for breakfast is a handful of pills."
TONYA MASON
MEDICAL MYSTERY: Tonya Mason was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis about two years after selling her home near the West Lake Landfill in Bridgeton, Missouri. There is no evidence linking the autoimmune disease to radiation, but she and other residents fear the dump’s radioactive waste made them sick. REUTERS/Eric Cox
Republic says none of those tests show unsafe levels of radiation that would cause people harm. The company continues to cite scientific studies, including the 2015 ATSDR report, as evidence that there is no need for a full cleanup.
Some current and past residents nearby don’t buy it. Melissa Mitchell – unrelated to cancer patient and neighbor Deborah Mitchell – moved with her two children into a three-bedroom ranch in Bridgeton in 1994. Eight years later, she was diagnosed with Grave’s disease, a thyroid condition. Her son developed a benign tumor the size of a tennis ball on his femur in 2012. Her dog died of stomach cancer. Mitchell wonders if all of their maladies were caused by radiation exposure.
Over the years, she says, she watched as neighbors fell ill all around her – next door, across the street, catty corner to her house. In five houses on the block, 10 people had cancer.
“I felt like I was living in a graveyard,” she told Reuters.
The EPA says it is now considering a plan that would require Republic and the other responsible parties to remove 94,200 cubic yards of radioactive-contaminated waste. That’s enough to fill 82 Boeing 747s.
Thirty-four years after the landfill’s designation as a Superfund site and more than eight years after the ATSDR published its report, the waste remains and trash continues to smolder underground. Because more off-site contamination has been uncovered, EPA administrators told Reuters they don’t know when the cleanup will begin. They say they hope it will be in the next decade.
How Reuters identified weaknesses in a US health agency’s work
By BENJAMIN LESSER, M.B. PELL and JAIMI DOWDELL
It is a little-known federal health agency with an unfamiliar name: the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Congress conceived it as part of the 1980 Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, commonly known as the Superfund law, meant to hold polluters responsible for the nation’s most toxic messes.
The law requires the agency to identify potential health risks at such sites to protect the people living and working around them. Reuters reporters had encountered several examples of the ATSDR failing its mission and decided to take a closer look.
To assess the agency’s work, they reviewed 428 health reports published on its website between 2012 and 2023. Those reports contained 1,582 conclusions regarding potential harms at Superfund sites or other concerns brought to the agency by communities or government agencies.
The agency often produces the reports in partnership with state agencies.
Reporters examined the ATSDR risk classification listed for each finding and categorized the conclusion: harm or potential harm found, no harm or no potential harm found, inconclusive findings. A handful of findings could not be categorized.
Fifteen people with expertise in environmental and public health vetted the Reuters methodology. They included former ATSDR employees, and state environmental health officials, academic researchers and community health advocates.
The data collected from the reports, available for download here, enabled the reporters to document:
How frequently the agency declared potential health hazards, found no hazard or failed to issue a conclusive finding.
How often the authors used outdated data to support their findings.
Reports in which the authors detailed serious limitations in the data or analysis that undermined their conclusions.
Reporters flagged reports for using outdated data when conclusions relied on data that was at least four years old. No federal standard exists for how fresh data must be to support health assessments like those the ATSDR produces. But generally, relying on data four years old or older would result in questionable findings, five public health and environmental regulatory specialists told Reuters.
For more information:
https://soundcloud.com/workweek-radio/ww-8...
Add Your Comments
We are 100% volunteer and depend on your participation to sustain our efforts!
Get Involved
If you'd like to help with maintaining or developing the website, contact us.
Publish
Publish your stories and upcoming events on Indybay.
Topics
More
Search Indybay's Archives
Advanced Search
►
▼
IMC Network