Concerning Humanity’s Future: Interview with Nick Humphrey, Climatologist and Geoscientist
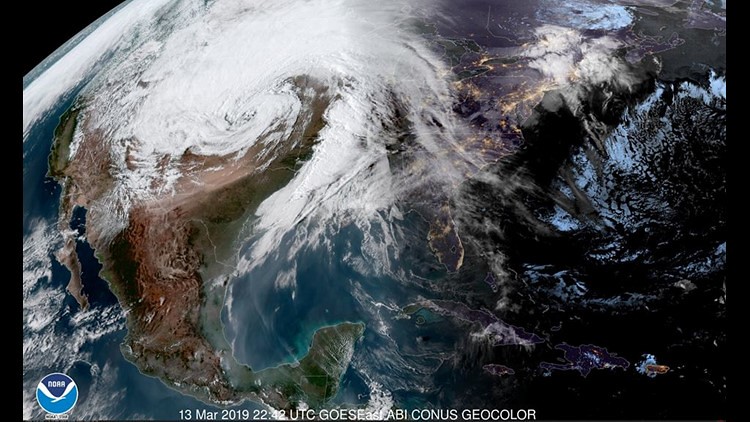 NOAA image of the “bomb cyclone” that struck the Midwest earlier this month, triggering flooding in three states and taking the lives of humans and livestock. The National Weather Service described it as “incredible” and a “Great Plains cyclone of historic proportions.”
NOAA image of the “bomb cyclone” that struck the Midwest earlier this month, triggering flooding in three states and taking the lives of humans and livestock. The National Weather Service described it as “incredible” and a “Great Plains cyclone of historic proportions.”
ML: Can you give us a brief summary of your background and why you became interested in studying the detrimental effects of climate change?
NH: My background is in meteorology, geosciences and interdisciplinary studies. I have a Bachelor of Science in Interdisciplinary Studies from South Dakota State University. I completed a Master of Science in Geosciences with a concentration in Applied Meteorology from Mississippi State University in 2016. My education and research studies have been in the societal impacts of weather/climate, natural hazards, and advanced forecasting techniques. I also have a background in global climatology. I did undergraduate research into human decision-making in response to tornado warnings and graduate research in tropical cyclone impacts. I have been following news and research into climate change for about the past decade. However, I became more intensive in my personal research as a result of an apparent acceleration in climate impacts in the past 4-5 yrs. My study took me to look into the research of scientists such as Dr. Natalia Shakhova, Dr. James White, Dr. Peter Wadhams, Dr. James Lovelock, and Paul Beckwith. I also looked into the interdisciplinary connections between ecological and environmental variables by Dr. Guy McPherson.
~~~~~~~~~~~
ML: What is the most disturbing aspect of anthropogenic global warming that you are seeing today and what are its implications for the future?NH: To me, the most disturbing aspect is the destruction of ice on the planet. It is commonly discussed among climate scientists that the planet has a high "inertia". This means in natural climate change, there is typically a significant lag between what is happening in the atmosphere (rise in greenhouse emissions) and climate response (warming of the planet), forcing a more gradual temperature rise. There are two very important components of Earth's inertia. 1) Water (which can gain/lose a huge amount of heat with a gradual temperature change) and 2) Ice. Ice, in my view, is the biggest climate regulator because it can do two things: 1) In the process of melting and freezing, heat is latent or "hidden". Meaning it does not contribute to temperature, but to melting (heat gain) or freezing (heat loss) of ice. 2) Ice is white, so as a result, it is a high reflector of visible light, preventing absorption of heat at the surface. So it has a double impact. As the planet loses ice because of warming temperatures, there is less total ice to melt and more heat goes into warming the oceans, land and atmosphere. It takes nearly 80 times more heat to melt ice than to warm the same amount of liquid water by 1 degree C/1.8 degrees F. The less ice there is, the lower the planetary albedo, resulting in more heat entering the climate system, creating a feedback loop to destroy ice faster and accelerating planetary heating. The loss of sea ice in the Arctic is a planetary catastrophe.

Trends in sea ice thickness are another important indicator of Arctic climate change. While sea ice thickness observations are sparse, here we utilize the ocean and sea ice model, PIOMAS (Zhang and Rothrock, 2003), to visualize mean sea ice thickness from 1979 to 2019. Updated through February 2019. https://sites.uci.edu/zlabe/arctic-sea-ice-volumethickness/
ML: With the environmental damage that has already been put into the pipeline, modern organized human society may not survive this century and we are already seeing signs of this with the destruction caused by recent extreme weather events. The city of Beira in Mozambique, recently hit by Cyclone Idai, is said to be "the first city to be completely devastated by climate change." Do you think it's possible to transition to a net-zero carbon emission civilization within a brief period? Would this not require a radical reconfiguration of every sector of our economy and the way in which we treat each other and the environment?
NH: In short, no, I do not think it is possible to transition to a net-zero carbon emission civilization within a decade. The idea itself is simply absurd because it would require basically returning to a pre-industrial society with none of the benefits which came from building the society provided by fossil fuels. There are some economists and environmentalists who believe you can have "green growth" but such growth leads to further environmental destruction as population and energy demands continue to grow exponentially. In order to go to a net-zero carbon civilization, you must first, ironically, increase carbon usage. More building of solar panels around the world, more building of wind farms, more building of electric cars, more concrete, more metal manufacturing, more highly polluting mining, not only of the land, but more rare Earth metals will be needed from the seas, harming ecosystems and polluting the oceans. Meanwhile, none of this stops climate change because, as you mention, there is already much damage in the pipeline. At 500 parts per million of equivalent carbon dioxide concentration, enough greenhouse gases are currently in the atmosphere to ultimately warm the planet 4-5 degrees C/7-9 F above 1700s temperatures, raise the sea level by 220 feet/67 meters (assuming 1 ppm CO2 equivalent = 1 ft sea level rise, based on past longer-term paleoclimate change response), remove significant amounts of soil moisture, leading to the destruction of agriculture. And this is without any other carbon releases or feedbacks. Building more in an attempt to maintain civilized society with high energy consumption makes this all worse.
~~~~~~~~~~~
ML: There are around 454 nuclear reactors around the world with several dozen more currently under construction. At least 100 U.S., European and Asian nuclear power stations are built just a few meters above sea level. With accelerated sea level rise and stronger storms on the horizon, we should be planning right now to decommission and close down these future nuclear disasters. What is your stance on nuclear energy?NH: Nuclear reactions themselves are an effective way to produce energy. The problem is that, like any form of energy, it requires energy to produce it and leaves waste products. Fossil fuels are needed to build the nuclear reactors (especially all the concrete), water is needed to keep the reactors fuel rods cool, and nuclear waste results from the use of the reactors which must be stored safely for thousands of years. It requires civilization to function for thousands of more years to keep it functional and safe or alternatively decades to properly decommission them. Given sea level rise is accelerating with a doubling of approximately 7-10 years (possibly causing a meter of sea level rise as early as the 2040s-2050s, faster in some regions like the US East Coast), I do not believe we should building more nuclear reactors and should decommission all others as quickly as possible to save what remains of the natural world from devastating impacts of nuclear failures if civilization collapses and humans are unable to care for those sites. I make note, it is not only nuclear power stations on coastal areas which are of concern. Stations located along rivers are at risk as well...from increasingly larger floods, drying rivers which are used for cooling, and warming rivers which do not bring in cool enough water to keep the reactors cool. These events are already happening.
~~~~~~~~~~~
ML: What do you think about geoengineering schemes by scientists to dim the sun in order to reduce global warming and buy humanity more time to "fix" the problem? Proposed technology that could pull CO2 out of the atmosphere at the scale required is generally considered a pipe dream. At what point do you think our civilization will lose faith in technology to solve all our problems?NH: Geoengineering schemes, to me, are equivalent to using a small band-aid for a large stab wound. It is and will be completely overwhelmed by what is happening. Spraying aerosols over the Arctic to try to cool the Arctic with increased summer cloud formation doesn't solve the fact that there is 500 ppm of equivalent carbon dioxide already in the atmosphere which cannot be removed with the speed and scale required. You are not dealing with regions where the geoengineering is being done in closed systems. You cool one area, other areas will respond by warming further. You cool one region, atmospheric and ocean circulations will develop and intensify to transport heat to the cooling area to try to equalize the temperature imbalance. Direct ocean heating from below the ice will make it difficult to grow thick ice and not allow ice to reform in the polar night. These heat balances have always existed of course, but it was still cool enough to allow significant ice to exist in the Arctic. The atmosphere is now too altered to allow widespread sea ice to exist in the near future and geoengineering doesn't prevent this or even delay it in a meaningful way.
~~~~~~~~~~~
ML: In the recent extreme flooding in the U.S. Midwest, farmers suffered devastating losses with similar food shocks on the rise around the world. How do you see the world feeding itself in such an uncertain future, especially when industrial monoculture is actually increasing worldwide?NH: In short, I do not see a way for humans to feed themselves in an organized manner. Using the worse-case estimate for warming since pre-industrial times, the planet's land air and sea surface has averaged around +1.2 C relative to pre-industrial the past 5 years with a peak of +1.4 C in 2016. The Northern Hemisphere land masses (where most of the food on the planet is grown) are quickly approaching +2 C. And we are already seeing the impacts of both extreme heat and extreme precipitation events on crops which depend on stability at mild temperatures and an expected range of moisture. This will only worsen and in between +1.5-2 C, we will conservatively see a reduction of US crop yields by between 30-46% of recent levels. By +4 C, that falls to 63-82% as aridification —droughts which are never-ending— dominate the Great Plains/Midwest and California Central Valley with very extreme summer heat and occasional intense rainfall as well as destructive flood events, exacerbating soil erosion. We are entering a range of weather conditions not supportive of agriculture. And not simply monoculture. All agriculture. Even other ways of doing Ag require stable weather conditions, seasonality, soils and ability to conduct economic activity between peoples. None of this will be possible in these conditions. And that assumes the ecosystems which support agriculture also remain stable and available and that is not likely given the ongoing global extinction of insects.
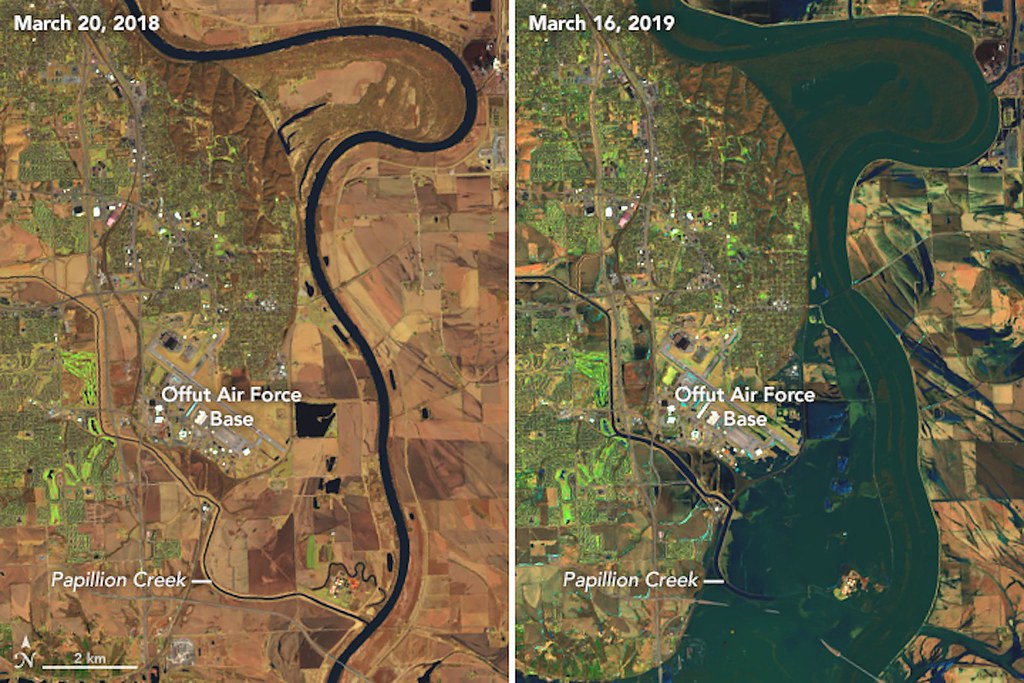
NASA Before/after imagery of flooding near Offutt Air Force Base, Nebraska.
ML: Many mainstream scientists feel that to “work within” the system, they have to use language that politicians and economists can understand in order to maintain credibility, i.e. the “value of ecosystem services”. Attempting to place a monetary value on every aspect of nature while externalizing the environmental cost of pollution is a major flaw of our economic system. Inaction by governments and corporations on climate change may have already condemned a large percentage of the global population to a premature death. Do you think ecocide should be an international crime?
NH: If ecocide were an international crime, we would all be guilty in some way. Obviously, I do not believe all humans are *equal* in terms of blame. A person living in the US is a far far larger consumer of energy with a bigger carbon footprint than a person in say, Kenya or Indonesia. And of course, the developing world receives cheap products (coal, plastics, etc) from the developed world. However, while greenhouse gas pollution is significant from countries such as the US and China, plastic pollution is significant *everywhere*. Mining pollution is significant everywhere. Deforestation either is or has been in the past significant from Canada to Europe, increasing in the Amazon, the continent of Africa, etc. Water is nearing depletion on the Great Plains, parts of Europe, Australia and falling quickly in the Amazon. We've required more energy on this planet for all the technologies which many would consider have enhanced human life and existence on this planet...improved infrastructure, medicines, monoculture farming which did allow for much higher and resilient production of crops, etc. But all of those "improvements" to the human condition come at a cost and that cost is the destruction of the natural world, and ultimately ourselves.
~~~~~~~~~~~
ML: I understand wealthy countries have much larger carbon footprints per capita than the rest of the world due to our unsustainable consumption patterns, but the other much overlooked factor is overpopulation. We are adding roughly 90 million more people onto the planet per year, many of whom are striving to attain a similar western standard of living. Is there any ethical way to control population growth or will nature be the final arbiter? What do you think is the maximum carrying capacity for the Earth's human population?NH: Overpopulation is a major problem and factor in the mass extinction ongoing on the planet. However, given the scales required to fix the problem, I do not see a way to fix it which would fix the damage already done to the planet within the timeframes necessary. The only *ethical* means to control overpopulation is to educate a free population (in particular, women must have reproductive freedom) on the benefits to humans by improving the natural world. Laws will fail because it is ultimately an issue of personal physical sovereignty and humans will always fight for personal sovereignty over their bodies as it relates to sex and reproduction vs. govt interference. China's one-child policy had a lot of unintended consequences. There are other ways to try to "control" but ultimately, what would really be needed is population decline. Given humans are a relatively large land mammal, in order for Earth to have kept ecosystem stability, the human population would have to have stayed in the millions, spread thinly across hospitable regions of the planet as hunter-gatherers. The population of hunter-gatherer/early agricultural humans in the Early Holocene (10-12,000 years ago) is estimated at 1-10 million. Ultimately, nature appears to be "loading the gun" to make it difficult for the human population to grow much longer; and really, it will crash. The 6th mass extinction is underway and humans will be a part of this given we are at the top of the food web.
~~~~~~~~~~~
ML: Who, living today, serves as a role model and inspiration for you and in what way? Do you follow any particular philosophy in your life?NH: I'd say one role model of mine is my father. He died in January 2017 after a battle with cancer. He spurred my interest in science as a child and was one who always strongly emphasized the importance of finding the truth, no matter how difficult it was or the barriers that happened to be in the way. Another is Dr. Albert Einstein, who had many personal flaws, but wanted to use science to improve society and found its uses for killing and destruction of life abhorrent. He spoke the truth even when it marginalized him. Also Dr. Neil DeGrasse Tyson, who works hard to communicate complex topics in a way that can be understood and appreciated by the average person. My only philosophy in life is to live my life to the fullest, given the incredible changes underway, and bring truthful information to people who can see what's happening and want to know "why?". I'm an interdisciplinarian and work to bring a more comprehensive understanding of the predicament we face to anyone willing to listen.
~~~~~~~~~~~
ML: What do you think of the Dark Mountain Project whose members have "stopped believing in the stories our civilization tells itself"? What new stories should we be telling ourselves in this age of ecological catastrophe and extreme economic inequality?NH: I'm not familiar with the Dark Mountain Project; however to answer the questions, I think we should stop telling stories about how grand our civilization is and celebrating its attempts to dominate nature and impose fake human superiority. Civilization, which served the purpose of insulating humans from the dangers Nature posed, has destroyed Nature at the expense of its own growth. This was true long before the development of the modern fossil-fueled world. In order to be sedentary and not be dependent upon the local forces of Nature, we needed to build towns and cities. This requires destroying forests, damming rivers, taking over land with agriculture we would control the growth and development of. This means other species, who could not stop us, lost territory. Each improvement in protecting ourselves from Nature meant more population growth, more resource needs, more energy, which in turn meant more destruction and more attempts at control. Humanity, as a hunter-gatherer species, meant our growth was dependent upon what we could find for food and water within the bounds of the climate. Our ability to enclose and mass manipulate our environment and resources meant we could grow beyond our resources and, in the process, mass pollute the world. Civilization has been an 8,000 year attempt to win a war against Nature. A war we are losing because Nature —following the laws which have governed the Universe for 14 billion years— always wins. Nature is in control, not humans. Even our current catastrophes which were sparked by humanity's activities were ultimately governed by the laws of Nature (physics, thermodynamics, chemistry, etc). We never were separate from it all, but a part of it. We should be telling ourselves to do what we feel is right to respect Nature and its unbreakable laws, accepting our place in the Universe as just one of many species which have a finite existence on this planet.
Nick Humphrey's blog can be found here: https://www.patreon.com/MeteorologistNickHumphrey
Get Involved
If you'd like to help with maintaining or developing the website, contact us.
Publish
Publish your stories and upcoming events on Indybay.